| |
|
|
 |
|
Advisory Committee on Health Effects of Endocrine Disruptors
The Supplement II to the Intermediary Report
1.1.4 |
| |
contents
Detailed contents
<< prev
next >> |
| |
4. Future tasks
(1) Screening
While tests related to estrogen receptors were given priority in
the earlier stage of this project because of restrictions of
time and technology, methods related to androgen and thyroid
receptors are now being emphasized. In fact, the necessity of
more comprehensive screening has been pointed out from the start
in view of the variety of endocrine receptors in humans. |
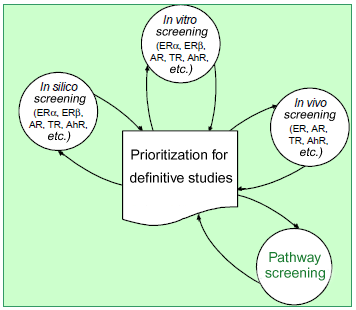
|
The test scheme is being enhanced to include various receptor
systems and studying effects on more than one system and
crosstalk between different systems more effectively. The
pathway screening12 using the microarray technique is a
candidate for the fourth screening technique which permits to
take into account the structure of proteins as well as receptors
that do not directly bind with molecules (see Figure). |
 |
|
The screening scheme is so designed as to exclude
pseudo-negatives while tolerating pseudo-positives. For example,
the receptor structure with pockets enlarged by binding with
antagonist molecules is used in the in silico screening to
reduce pseudo-negatives. Since the prioritization is made by
sorting the results of a battery of screening tests, the
criterion for positive/negative decision need not necessarily be
established for individual tests. However, the criterion may be
revised as new data are added in order to improve the precision
(i.e. to minimize the number of pseudo-negatives). |
|
| |
12
The pathway screening is a screening technique consisting of the
following three steps: (i) building a toxico-genomic database,
based on animal experiments of a relatively large scale, which
contains information on the profiles and pathways of gene
expression triggered by typical ligands (e.g. hormones) to the
intranuclear receptors; (ii) administering the substance tested
to a small number of animals to obtain gene expression profiles
for appropriate target organs by toxico-genomic techniques; and
(iii) comparing the results with data from the database ((i)
above) to determine the pathway of action of the substance in
question. This method permits more comprehensive screening for a
more variety of receptor systems.
The toxico-genomic database is under construction in cooperation
with a separate program of Toxico-Genomics for Chemical Safety. |
|
|
|
contents
Detailed contents
<< prev
next >> |
|
|
|
